
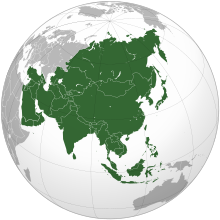
 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured articleOn the night of 9/10 March 1945, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) conducted a devastating firebombing raid on Tokyo, the Japanese capital city. This attack was code-named Operation Meetinghouse by the USAAF and is known as the Great Tokyo Air Raid in Japan. Bombs dropped from 279 Boeing B-29 Superfortress heavy bombers burned out much of eastern Tokyo. More than 90,000 and possibly over 100,000 Japanese people were killed, mostly civilians, and one million were left homeless, making it the most destructive single air attack in human history. The Japanese air and civil defenses proved largely inadequate; 14 American aircraft and 96 airmen were lost. The attack on Tokyo was an intensification of the air raids on Japan which had begun in June 1944. Prior to this operation, the USAAF had focused on a precision bombing campaign against Japanese industrial facilities. These attacks were generally unsuccessful, which contributed to the decision to shift to firebombing. The operation during the early hours of 10 March was the first major firebombing raid against a Japanese city. The USAAF units employed significantly different tactics from those used in precision raids, including bombing by night with the aircraft flying at low altitudes. The extensive destruction caused by the raid led to these tactics becoming standard for the USAAF's B-29s until the end of the war. (Full article...)Selected Country Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country mostly in Central Asia, with a part in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbekistan to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southwest, with a coastline along the Caspian Sea. Its capital is Astana, while the largest city and leading cultural and commercial hub is Almaty. Kazakhstan is the world's ninth-largest country by land area and the largest landlocked country. It has a population of 20 million and one of the lowest population densities in the world, at fewer than 6 people per square kilometre (16 people/sq mi). Ethnic Kazakhs constitute a majority, while ethnic Russians form a significant minority. Officially secular, Kazakhstan is a Muslim-majority country, although ethnic Russians in the country form a sizeable Christian community. Kazakhstan has been inhabited since the Paleolithic era. In antiquity, various nomadic Iranian peoples such as the Saka, Massagetae, and Scythians dominated the territory, with the Achaemenid Persian Empire expanding towards the southern region. Turkic nomads entered the region from as early as the sixth century. In the 13th century, the area was subjugated by the Mongol Empire under Genghis Khan. Following the disintegration of the Golden Horde in the 15th century, the Kazakh Khanate was established over an area roughly corresponding with modern Kazakhstan. By the 18th century, the Kazakh Khanate had fragmented into three jüz (tribal divisions), which were gradually absorbed and conquered by the Russian Empire; by the mid-19th century, all of Kazakhstan was nominally under Russian rule. Following the 1917 Russian Revolution and subsequent Russian Civil War, the territory was reorganized several times. In 1936, its modern borders were established with the formation of the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic within the Soviet Union. Kazakhstan was the last Soviet republic to declare independence during the dissolution of the Soviet Union from 1988 to 1991. (Full article...)Featured biographyAbu Ali Salih ibn Mirdas (Arabic: ابو علي صالح بن مرداس, romanized: Abū ʿAlī Ṣāliḥ ibn Mirdās), also known by his laqab (honorific epithet) Asad al-Dawla ('Lion of the State'), was the founder of the Mirdasid dynasty and emir of Aleppo from 1025 until his death in May 1029. At its peak, his emirate (principality) encompassed much of the western Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia), northern Syria and several central Syrian towns. With occasional interruption, Salih's descendants ruled Aleppo for the next five decades. Salih launched his career in 1008, when he seized the Euphrates river fortress of al-Rahba. In 1012, he was imprisoned and tortured by the emir of Aleppo, Mansur ibn Lu'lu'. Two years later he escaped, capturing Mansur in battle and releasing him for numerous concessions, including half of Aleppo's revenues. This cemented Salih as the paramount emir of his tribe, the Banu Kilab, many of whose chieftains had died in Mansur's dungeons. With his Bedouin warriors, Salih captured a string of fortresses along the Euphrates, including Manbij and Raqqa, by 1022. He later formed an alliance with the Banu Kalb and Banu Tayy tribes and supported their struggle against the Fatimids of Egypt. During this tribal rebellion, Salih annexed the central Syrian towns of Homs, Baalbek and Sidon, before conquering Fatimid-held Aleppo in 1025, bringing "to success the plan which guided his [Banu Kilab] forebears for a century", according to historian Thierry Bianquis. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured pictureAn Adivasi (indigenous) woman from the Kutia Khond tribal group in the Indian state of Orissa. Khonds were known for their human sacrifices, which were intended to further the fertilization of the earth.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
Birds and flowers of the four seasons (紙本墨画花鳥図, shihon bokuga kachōzu), part of the Paintings on room partitions in the abbot's quarters (hōjō) (方丈障壁画, hōjō shōhekiga) of Jukō-in (聚光院) of Daitoku-ji (大徳寺), Kyoto, Japan. Ink on paper. This picture shows four of 16 panels on fusuma (sliding doors) in the ritual room (室中). The paintings have been designated as National Treasures of Japan in the category paintings. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |






























































































